The Magic of Storytelling
More than Reading - A Seasonal Invitation to Connect as a Family
by Maria Montes, Kim Mason & Laina Sorensen: Primary 1 Guide & Assistants
Monday, January 5, 2026
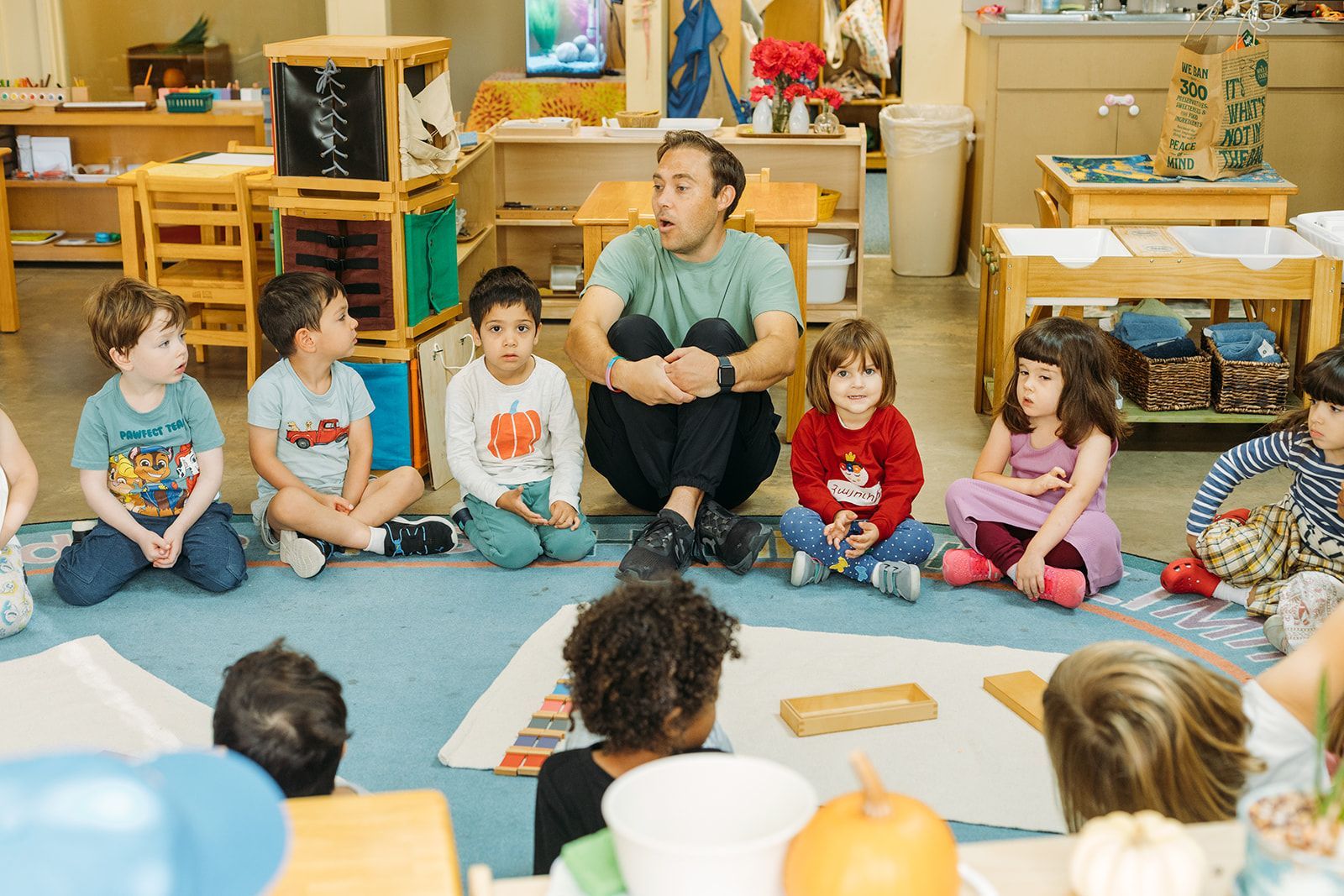

Storytelling is one of the oldest and most powerful ways children learn. Long before books existed, families shared stories to teach lessons, explain the world, and connect with one another. Today, research continues to show that storytelling plays a vital role in children’s learning, imagination, and emotional growth.
Our brains naturally respond to stories. When children listen to a story, they don’t just hear words - they picture scenes, feel emotions, and make meaning. This is why stories help children remember information more easily and understand ideas more deeply than through facts alone.
Why Storytelling is So Important for Young Children
- Builds strong listening skills
- Strengthens memory and attention
- Encourages imagination and creativity
- Supports emotional understanding and empath
- Helps children understand real-world situations
- Boosts confidence in speaking and oral language
Through stories, children learn to recognize feelings, solve problems, and understand different perspectives - all essential life skills. Storytelling creates a warm, personal connection between the adult and child. With eye contact, gestures, and expressive voices, children feel truly engaged. Because there are no pictures, children use their own imagination to create the story in their minds, which builds creativity, listening skills, and emotional connection.
Why Stories Stay with Us
Stories help children understand the world and their place in it. When adults share stories - real or imagined - children feel valued and connected. Storytime becomes more than learning; it becomes a moment of bonding, comfort, and joy. Storytelling also fosters curiosity and wonder, which are at the heart of lifelong learning.
How Families Can Support Storytelling at Home
- Share stories from your own childhood
- Make up silly or imaginative stories together
- Let your child tell you their own stories
- Talk about feelings and choices in stories
- Enjoy reading books together every day
Every story you share helps build your child’s language, confidence, and love for learning.
Storytelling is not just something we do - it is a part of who we are. When we tell stories to children, we pass along the gift of imagination, connection, and learning that has shaped humanity for generations. This is also the perfect time of year to enjoy family gatherings and share stories together. These moments - filled with laughter, memories and meaningful conversations - become treasures that children carry in their hearts for years to come. The stories shared today become the memories passed down tomorrow, from one generation to the next.